Fracture and Treatment of fractures
A fracture is a break or a crack in a bone. It can be complete or incomplete. A fracture is caused by a force exerted against a bone which is stronger than the bone can structurally withstand. The common types of forces are mechanical falls, motor vehicle accidents, and falling from heights.
The most common fractures are the wrist, ankle and hip fractures. Incidence of fractures is high in older ages and in children.
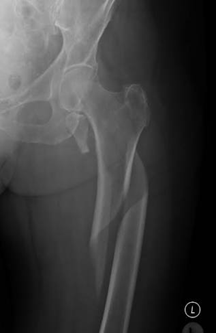
Treatment includes restriction of activities, immobilising the bone with a plaster cast, or surgically inserting metal rods or plates to hold the bone pieces together.
Treatment of fractures varies from fracture to fracture, as well as patient to patient. In orthopaedics we talk about “Fracture Personality” and “Patient Personality”.
Children’s fractures are of special significance due to the fact that often the fracture is through, or close to, the growing area of the bone(called Growth Plate).Injuries to the growth plate can lead to growth retardation (resulting in shortening of the limb) or developing a progressive deformity as the child grows.




